The question of whether college education should be free or not is a controversial one, with strong arguments on both sides. On the one hand, supporters of free college education argue that it would increase access to education, reduce student debt, and improve economic equality. On the other hand, opponents of free college education argue that it would increase the tax burden, lower the quality of education, and disincentivize private institutions. Additionally, there would be an impact on teachers, with increased demand for their services and a potential decrease in salary. In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of free college education and its impact on teachers, and attempt to draw a conclusion on this complex issue.
Contents
- Pros of Free College Education
- Cons of Free College Education
- Impact on Teachers
- Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions
- FAQs
- 1. Will free college education eliminate student debt completely?
- 2. How will free college education affect the quality of education?
- 3. Who will fund free college education?
- 4. Will free college education lead to an increase in taxes?
- 5. Will free college education be available to everyone?
- 6. How will free college education affect private institutions?
- 7. Will free college education lead to an increase in demand for teachers?
- 8. Will free college education lead to a more educated workforce?
- 9. How will free college education affect the job market?
- 10. What are the potential drawbacks of free college education?
- References
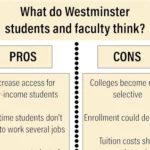
Pros of Free College Education

Free college education has numerous benefits for students and society as a whole. Firstly, it increases access to education for a wider range of students, allowing individuals from all socioeconomic backgrounds to receive a college degree. Secondly, it reduces student debt, enabling graduates to start their careers without the burden of heavy loan payments. Lastly, it contributes to improved economic equality, creating a more equitable society. Free college education has the potential to transform the lives of millions of people, providing them with opportunities that were previously out of reach.
1. Increased Access to Education
One of the most significant benefits of free college education is the increased accessibility to higher education. Many students are unable to attend college due to the high costs of tuition, room, and board. As a result, some students are forced to take out large loans, which can lead to long-term debt. In fact, student loan debt has reached an all-time high in recent years, with many students struggling to pay off their loans well into their thirties and forties.
By making college free, more students would have the opportunity to pursue higher education without the burden of financial stress. This would not only benefit individuals but also society as a whole. With more students able to attend college, there would be an increased number of skilled workers in various fields, leading to a more educated and productive workforce.
Free college education would also provide more opportunities for students from disadvantaged backgrounds. Many low-income students are unable to afford college, which limits their future career prospects. With free college education, these students would have an equal opportunity to pursue higher education and achieve their career goals.
However, it is important to note that free college education alone may not be enough to increase access to education for all. Other barriers, such as standardized testing and lack of resources in low-income schools, also need to be addressed to ensure equal access to education for all students.
2. Reduced Student Debt
One of the main advantages of free college education is that it can significantly reduce the amount of student debt that students accumulate. With the high cost of tuition, textbooks, and other fees, many students graduate with thousands of dollars in debt, which can take years or even decades to pay off. Free college education can eliminate this burden, allowing students to focus on their studies and pursue their career goals without the added stress of debt. This can also have a positive ripple effect on the economy, as graduates are more likely to invest in homes, cars, and other goods and services, which can stimulate growth and create jobs. However, it is important to note that free college education may not be a cure-all for student debt, as other expenses such as housing, food, and transportation can still be significant barriers for low-income students. Additionally, some argue that free college education may lead to a decrease in the value of a college degree, as more people would have access to it, potentially lowering the earning potential of graduates. While reduced student debt is a compelling argument for free college education, it is important to consider the potential drawbacks and limitations.
3. Improved Economic Equality
Providing free college education can improve economic equality by eliminating financial barriers that prevent low-income students from pursuing higher education. When college education is made affordable, students from all backgrounds can access quality education and improve their job prospects. This can lead to a more diverse and skilled workforce, which can boost economic growth and development. By providing equal opportunities to all students, free college education can help reduce income inequality, as education is one of the key factors that determine earning potential. Studies have shown that college graduates earn significantly more than those without a degree, and by making college education accessible to everyone, free college education can help close the income gap. This can lead to a more just and fair society, where everyone has an equal chance to succeed regardless of their socioeconomic background. However, it is important to note that free college education alone may not be enough to address all the root causes of economic inequality, and more comprehensive policies may be needed to address issues such as systemic racism and discrimination.
Cons of Free College Education

One of the cons of free college education is the increased tax burden it would place on society. While the idea of free education may seem appealing, it would require significant funding from the government, which would likely come in the form of increased taxes. This could lead to resistance from taxpayers who do not want to shoulder the burden of funding higher education for all. Additionally, critics argue that free education could have a negative impact on the quality of education. Without the financial incentives to attract students, private institutions may struggle to compete with free public colleges, potentially leading to a decline in the quality of education overall.
1. Increased Tax Burden
One of the major arguments against free college education is the increased tax burden that would be placed on taxpayers. The cost of providing free college education would be significant, and it would require a substantial increase in government funding. This would most likely result in higher taxes for individuals and businesses, which could have a negative impact on the economy. Additionally, some argue that the tax burden would be unfair, as it would require those who did not attend college to pay for the education of those who did. This could lead to resentment and a lack of support for the program.
However, proponents of free college education argue that the benefits of increased access to education and reduced student debt outweigh the potential costs. They also point out that many other countries, such as Germany, offer free college education and have not experienced negative consequences from increased taxes. It is important to consider both sides of the argument and weigh the potential costs and benefits before making a decision on whether or not to implement free college education.
Related link: Why Should Phones Not be Allowed in School?
2. Lower Quality of Education
One of the potential downsides of free college education is a lower quality of education. With more students attending college, there may be a strain on resources, including faculty, facilities, and funding. These strains could lead to larger class sizes, fewer course offerings, and less individual attention for students. In turn, this could result in a less robust learning experience and lower-quality education. Additionally, with less funding available, colleges may have to cut back on programs and resources that contribute to the overall quality of education. This could include research programs, extracurricular activities, and student support services.
However, it’s important to note that this is not a guaranteed outcome. Some proponents of free college argue that increased funding and resources could offset any potential negative effects on the quality of education. Additionally, with more students attending college, there may be a greater demand for skilled workers, which could lead to increased funding for education and research.
While the possibility of a lower quality of education is a concern, it’s not a definitive outcome of free college education. It’s important to weigh the potential benefits and drawbacks and consider how they would impact the overall education system.
3. Disincentivize Private Institutions
One of the main arguments against free college education is that it would disincentivize private institutions. Private colleges and universities rely on tuition fees to fund their operations. If college education were to become free, these private institutions would lose a significant portion of their student body and revenue. This could have negative consequences for the quality of education they provide, as they may not have the resources to maintain their current standards.
Private institutions often offer specialized programs and degrees that are not available at public institutions. These programs may be more expensive to operate and would likely become less viable if college education were to become free. This would limit the diversity of educational options available to students.
Private institutions often have more flexibility in their admission policies and can offer more personalized attention to their students. With free college education, public institutions may become more crowded and less able to offer individualized attention to their students.
While free college education may increase access to education, it could have negative consequences for the diversity and quality of educational options available to students. It is important to consider these potential drawbacks when evaluating the feasibility of free college education policies.
Impact on Teachers
With the implementation of free college education, there would be a significant impact on teachers. Firstly, there would be an increased demand for teachers to teach the growing number of students in colleges. Secondly, with a more educated workforce, the level of education of teachers would need to be increased, leading to more advanced degrees and certifications. Finally, there is a potential salary decrease for teachers as they may not be receiving the same level of payment as they would in private institutions. Despite these potential drawbacks, the benefits of free college education for society as a whole cannot be ignored.
1. Increased Demand for Teachers
One of the potential impacts of free college education is an increased demand for teachers. With more students attending college, there will be a need for more educators to teach these students. This could lead to an increase in job opportunities for teachers, especially in fields such as science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM).
However, this increased demand for teachers could also lead to challenges in finding enough qualified educators to fill these positions. The teaching profession may become more competitive, and there may be pressure to lower standards for teacher qualifications to meet demand. Additionally, an increase in demand for teachers could also lead to an increase in class sizes, which could make it more difficult for teachers to provide individualized attention to students.
While free college education could lead to an increase in demand for teachers, it is important to consider the potential challenges and limitations that could arise from this increased demand. It is crucial to ensure that there are enough qualified teachers to meet the needs of students and that the quality of education is not compromised.
2. More Educated Workforce
One of the biggest pros of free college education is the potential for a more educated workforce. With more individuals having access to higher education, there could be an increase in the number of skilled workers in various fields. This could lead to a more competitive job market and potentially drive innovation in industries that require high levels of education and specialization. A more educated workforce could result in a stronger economy as a whole, as individuals with higher levels of education tend to earn higher salaries and contribute more to the economy through taxes and spending.
However, it is important to note that simply making college education free does not guarantee a more educated workforce. There are still many factors that can impact whether or not individuals are able to complete their education, such as personal circumstances, social and economic barriers, and academic preparedness. Additionally, if free college education leads to a significant increase in the number of individuals pursuing higher education, there could be challenges in terms of providing enough resources and support to ensure that students are able to succeed.
While free college education has the potential to lead to a more educated workforce and a stronger economy, it is important to consider the potential challenges and limitations of such a policy.
3. Potential Salary Decrease
One of the potential downsides of free college education is the impact it could have on teacher salaries. If more people are entering the education field due to the increased demand for teachers, this could lead to a surplus of teachers and potentially drive down salaries. Additionally, as public institutions may not have the same funding as private institutions, there may be less money available for teacher salaries, which could further exacerbate the issue. It’s important to consider the potential long-term effects of free college education on the teaching profession and whether it could ultimately lead to a decrease in teacher salaries and potentially dissuade talented individuals from pursuing a career in education.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the question of whether college education should be free is a complex one with valid arguments on both sides. The pros of free college education include increased access to education, reduced student debt, and improved economic equality. On the other hand, the cons of free college education include an increased tax burden, lower quality of education, and disincentivizing private institutions. Additionally, free college education would have an impact on teachers, including an increased demand for teachers, a more educated workforce, and potential salary decrease. While there is no clear answer, it is important to consider all factors and potential consequences before making a decision on whether to implement free college education.
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about free college education:
1. Will free college education eliminate student debt completely?
While free college education can reduce student debt, it may not eliminate it completely. Students may still need to pay for other expenses such as room and board, textbooks, and other fees.
2. How will free college education affect the quality of education?
Free college education may lead to a lower quality of education due to a potential increase in demand for resources and a decrease in funding for private institutions. However, this will depend on how the program is implemented and funded.
3. Who will fund free college education?
The funding for free college education will most likely come from taxes or government budgets. However, it may also come from private donors or partnerships with private institutions.
4. Will free college education lead to an increase in taxes?
Free college education may lead to an increase in taxes to fund the program. However, it may also lead to a decrease in taxes in the long run due to the economic benefits of a more educated workforce.
5. Will free college education be available to everyone?
The availability of free college education will depend on the specific program and its eligibility requirements. Some programs may only be available to low-income students or those who meet certain academic criteria.
6. How will free college education affect private institutions?
Free college education may disincentivize private institutions and lead to a decrease in funding and resources for these institutions. However, it may also lead to new partnerships and collaborations between private and public institutions.
7. Will free college education lead to an increase in demand for teachers?
Free college education may lead to an increase in demand for teachers due to the potential increase in enrollment. However, it may also lead to a decrease in demand for teachers in certain fields or institutions.
8. Will free college education lead to a more educated workforce?
Free college education may lead to a more educated workforce, which can lead to economic benefits such as increased productivity and higher wages. However, this will depend on the quality of education and the specific program.
9. How will free college education affect the job market?
Free college education may lead to a more competitive job market due to an increase in the number of educated workers. However, it may also lead to new job opportunities in certain fields or industries.
10. What are the potential drawbacks of free college education?
Potential drawbacks of free college education include an increase in taxes, a lower quality of education, and a decrease in funding for private institutions. It may also lead to a decrease in the value of a college degree and a decrease in diversity among students.